An Overview Of Patient Service Programs Technology
By Mathini Ilancheran, senior delivery lead - research, R&D, Beroe Inc.

Any service that helps keep patients in a clinical trial falls under the patient services category. The major patient support services or programs used by pharmaceutical companies concern patient adherence, patient access, patient affordability, and patient advocacy. The description of each is below:
- Patient affordability programs provide free or discounted drugs and/or financial assistance to uninsured and underinsured patients to cover their medication costs.
- Patient adherence programs help to actively engage with patients and involve them in the treatment, thereby improving adherence to trial protocol.
- Patient access programs include denial management, payment estimation, and streamlining pre-registration, among others.
- Patient advocacy ensures patient's rights and privacy are maintained, informed consent is obtained, awareness building, and patient education, among others.
In addition to the above, patient recruitment and retention services also fall under the patient services category as described below.
- Patient databases are registries, health databases, observational data, data from social media and communities, etc. that are used to build a network of patient details that are used to connect to people during trials.
- Home care services and direct-to-patient deliveries are a step toward patient-centric trials, in which kits are sent to and samples are collected from the patient's home.
- Patient engagement support includes the use of wearables, telemedicine, and personalized patient portals, among others.
Defining Technology Trends In Patient Services
Pharma companies are evolving their patient-centric approach by integrating technology and developing software that ensures patients are adherent to their medications, overcome financial burdens, and receive the medications via alternate payment options. Table 1 below provides an overview of the technologies integrated among patient services.
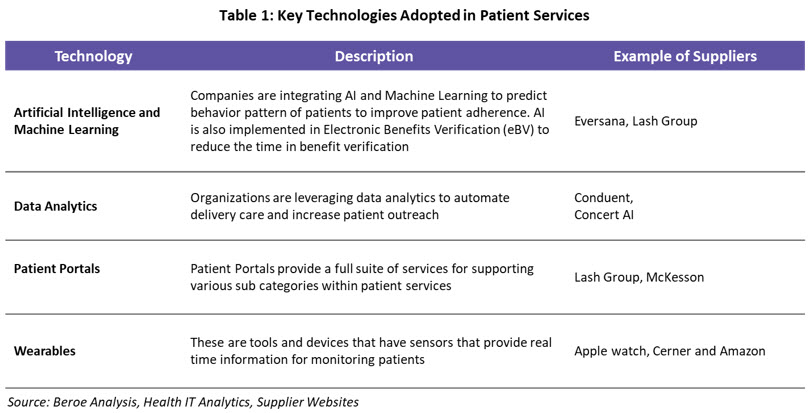
Some of the key technology and innovation trends within the patient services category are:
- Electronic Benefit Verification — Widely adopted in electronic benefit verification (eBV), artificial intelligence is helping to evolve the process workflow and accelerate the speed of therapy to patients. eBV has reduced the lead time between the patients and payers. Integration of AI with eBV will automate the entire process and provide critical pharmacy coverage information at a faster rate without any hassle.
- Co-pay — Digital tools are commonly used among co-pay programs. There are predictor tools that enable patients to identify brands that are impacted by accumulators and identify alternate payment options and adherence support for at-risk patients. A few tools are helping patients overcome financial issues to minimize the accumulator burden.
- Patient Engagement — This category uses the following technologies:
- Online portals — The adoption of patient health portals is still growing at a modest rate. It is a place where patients go to confirm appointments, fill out their medical and social history forms, update health records, view lab results, and pay any outstanding balances.
- Mobile applications — Mobile health applications provide real-time access to support patient engagement. According to a survey by SOTI, about 57% of physicians offer their patients a mobile app to schedule appointments, access personal healthcare information, and view lab results.1
- Chatbots — Chatbots are an AI-assisted tool that patients can communicate with via a chat window on a website or by phone to receive assistance with their inquiries. Chatbots can be used to schedule follow-up appointments with a patient's clinician online.2
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) — Communication via text or voicemail provides a way for health groups to reduce no-shows, as well as eliminate outstanding balances. A patient can confirm an appointment or even be forwarded to a call center to process a credit card payment.
- Call centers — Hospitals and other medical practices use third-party organizations to call patients before their appointment time to collect the data required for their visit. Medical history and other data are collected by a call center agent and entered directly into the care facility's registration system and EHR for storage and later use.
- Kiosks — Kiosks have great potential for collecting patient information. Despite their many available forms (free-standing kiosks, tablets, and laptops) kiosks have yet to see the adoption rate expected by some within the healthcare industry.
- Home Healthcare Services — Online portals and mobile applications are used here to allow people with health conditions to share health information and communicate with other patients, improving engagement between physician and patient. A collection tool, including an easy-to-use mobile app and an online portal, has been validated for use in clinical trials.
- Patient Adherence & Patient Support Services — The adoption rate of technologies is highest here, including:
- Smart boxes — Companies are developing electronic technology for medication adherence monitoring during trials. For example, Schreiner’s therapy monitoring technology consists of smart blister packs and smart kit boxes with sensor technology that is linked to its software and provides real-time information regarding the dosing history. Patch Rx has developed a smart pill bottle cap that tracks when a patient takes the medication, and the pharmacist can access this data via its web application and remind the patient in case they don’t adhere to their medication regimen. The Med-Con technologies mobile app uses the barcode on existing medication packaging (bottles, blisters, inhalers, injections, liquids, topical creams), to capture and measure patient adherence. It allows patients to use their own mobile which is more cost effective to the pharma company.
- Wearables — Wearable devices help track and monitor patients and record real-time data, which helps the pharma company to monitor the patient’s progress and decide how to provide personalized care.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) — Predictive algorithms can identify nuances around patient non-adherence, allowing care teams to pinpoint root causes and intervene in a timely way to improve outcomes.3
- Telehealth — Telehealth provides a popular alternative healthcare option to the traditional healthcare setting. Next-generation telehealth medicine uses a telemedicine cart and telehealth software to manage, analyze, or visualize the patient’s data. Telehealth allows patients to contact doctors remotely using smart devices for services like mental health support, chronic disease management, and diagnostic assessments.
- Data analytics — Using data analytics to estimate the use of copay programs by patients will help pharma companies to optimize programs. Patient compliance and patient enrollment can be planned with the help of analytics tools, which will attract patients to use branded drugs.
- Digital support — Pharma companies are actively adopting new technologies and increased use of e-prescribing for distributing co-pay offset programs. While text messages and emails are used for refill reminders and educational materials, social media became the go-to channel for providing coupon codes to patients.
- Natural language processing (NLP) — Cardinal Healthcare used NLP to analyze all the data it had collated from patient calls. This enabled the company to identify challenges and barriers that their patients were facing. By processing large amounts of patient data, NLP allows companies to identify patient challenges and barriers, like risk factors, to inform tailored treatment recommendations.3
Conclusion
The industry is moving toward integration of AI and machine learning (ML) and many organizations are looking forward to integrating various forms of digital tools to automate part of the patient services process within the next five years. Remote patient monitoring, mHealth tools, and portals have been long present in the market and explored, but companies are still trying to integrate AI/ML to create a database to later leverage predictive analytics to improve patient outcomes.
The pharma industry can engage with upcoming data analytics technology service providers to streamline the healthcare system with a centralized source of data procurement. This will enable all participants in the healthcare ecosystem to access the same medical data.
References:
- SOTI, "Patients say physicians with mobile apps are faster, convenient, offer better communication," 2019. [Online]. Available: https://soti.net/resources/newsroom/2019/patients-say-physicians-with-mobile-apps-are-faster-convenient-offer-better-communication/. [Accessed December 2023].
- A. Tapia, "6 uses of AI in healthcare: Healthcare bots," 2019. [Online]. Available: https://medium.com/@atapia_78342/6-uses-of-ai-in-healthcare-healthcare-bots-ac101b2a43a7. [Accessed December 2023].
- H. Jenner, M. Hackenberg and A. W. Roeser, "The Role of Patient Organizations in Accelerating Innovation in Patient Care Through Artificial Intelligence – Pt. 1," 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.iqvia.com/locations/united-states/blogs/2023/10/the-role-of-patient-organizations-in-accelerating-innovation-in-patient-care-through-ai-pt-1. [Accessed December 2023].
- T. Shaik, X. Tao. N. Higgins, L. Li, R. Gururajan, X. Zhou and U. R. Acharya, "Remote patient monitoring using artificial intelligence," WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2023.
- [x]cube LABS, "NLP in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Patient Care with Natural Language Processing.," [Online]. Available: https://www.xcubelabs.com/blog/nlp-in-healthcare-revolutionizing-patient-care-with-natural-language-processing/.
About The Author:
 Mathini Ilancheran is the principal analyst of R&D for Beroe Inc. She specializes in understanding market scenarios across the globe in the outsourcing arena. Her analysis has enabled global fortune 500+ companies in their strategic decisions on supply base optimization, risk reduction, innovation and efficient sourcing. She has written for several publications related to R&D procurement opportunities. With her category knowledge, she has published 35+ articles in leading journals, co-authored with industry experts. She has a master's in management from University College London (UCL) and has worked as a consultant in the U.K. You can contact her at mathini.ilancheran@beroe-inc.com and connect with her on LinkedIn.
Mathini Ilancheran is the principal analyst of R&D for Beroe Inc. She specializes in understanding market scenarios across the globe in the outsourcing arena. Her analysis has enabled global fortune 500+ companies in their strategic decisions on supply base optimization, risk reduction, innovation and efficient sourcing. She has written for several publications related to R&D procurement opportunities. With her category knowledge, she has published 35+ articles in leading journals, co-authored with industry experts. She has a master's in management from University College London (UCL) and has worked as a consultant in the U.K. You can contact her at mathini.ilancheran@beroe-inc.com and connect with her on LinkedIn.
