Analyzing The Top Clinical Trial Technology Trends
By Mathini Ilancheran, senior delivery lead - research, R&D, Beroe Inc.

Technology plays a critical role in drug development and the R&D value chain by revolutionizing clinical trials and decreasing the failure rate. Though the supply of technology has been increasing and regulation of innovative methods is easing, pharmaceutical companies have been slow to use the emerging technologies, due to the ambiguity prevailing around this space and a highly fragmented supply market. This article outlines the key technologies that have a high impact across trial phases.
Increased clinical trial costs, coupled with a higher percentage of trial failures and an increase in patient-centric trials, have caused a surge in demand for technology adoption in clinical trials. The below are the main industry challenges technology can address:
- Incomplete patient enrollment: This prevails in nearly 48 percent of sites despite a large amount of resources allocated (around 30 percent) to patient recruitment
- Long and delayed trial process: Long clinical trial timelines occur due to inefficient data manage
![]() ment and lack of evidence on patient outcomes
ment and lack of evidence on patient outcomes - Low clinical trial success rate: Trial failure occurs around 10 to 13 percent on average, with Phase 2 to Phase 3 being a challenging transition for the majority of drug candidates
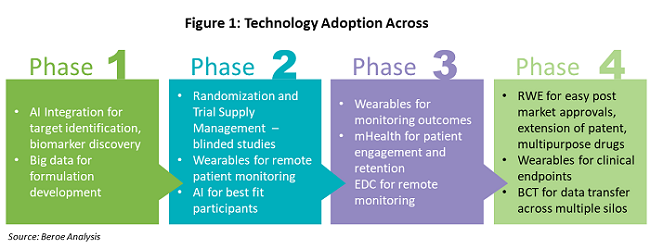
Figure 1 shows the various technologies that are being adopted throughout the drug development phases.
Global R&D Technology Market
Use of technologies in the R&D market is growing at the rate of around 22 to 23 percent, owing to the various organizational and clinical trial implications, and technology adoption has proved to be time- and cost-efficient for sponsors. Figure 2 shows the estimated growth of the global technology market through the period 2018 – 2023. The key applications of technology within clinical trials are real-world data capture (or real-world evidence, RWE), improved patient adherence, faster patient enrollment, and better trial data analytics.

Presently, North America comprises around 40 percent of the R&D technology market and is expected to grow significantly in the next five years. Europe is the next largest contributor, with about 25 percent of technology adoption, due to robust infrastructure and widespread use of mobile devices and EHRs. APAC’s contribution, although relatively low, is forecasted to increase over the period due to the rise of clinical trials in that region, especially in China, India, Japan, and the Philippines.
Trends Driving Technology Adoption
Patient-centric trials: Disruptive technologies like wearables, mHealth, and RWE have paved the way to conducting smaller trials. From patient enrollment to drug administration and follow-ups, everything is executed through a phone given to trial participants. For example, Science 37 recently conducted Phase 2 siteless trials through its Network Oriented Research Assistant (NORA) app with AOBiome for acne - which not only cut patient enrollment time by 50 percent but also generated a diverse pool of participants and insightful clinical endpoints.
Automation to remain competitive: Recently, there has been increased spending by pharma companies on AI and Big Data analytics, given their transformative power over the R&D process and the cost savings they enable. Competition in the market, in addition to business transformation and agility, is one of the key forces driving huge investments.
Ingestible sensors to target adherence: Increased impact on treatment adherence has been one of the key reasons for surging interest in technology by pharma companies. Introduction of wearables and ingestible sensors like Abilify MyCite and the use of AI-driven chatbots to monitor patient outcomes are all evidence that this trend is thriving in pharma R&D. For example, Janssen is collaborating with Scripps Translational Science Institute, Aetna, and iRhythm Technologies to remotely detect aFIB using mHealth screening to prevent strokes.
Market collaborations for virtual clinical trials: Pharma companies are increasingly adopting technologies through collaborations with major players in the market. This greatly increases the traditional global participation of only 3 percent in clinical trials. For example, Boehringer Ingelheim is collaborating with Science 37 to use the NORA platform to conduct remote clinical trials.
Trending Technologies
Following are a few of the technologies that are expected to revolutionize patient enrollment, patient engagement, trial data management, and collection of endpoint data for easy post-market approval.
Artificial Intelligence (Growth Stage)
Investment in AI technology for pharma R&D is greatly increasing given the evolution of supplier maturity and its ability to streamline clinical trial operations. The presence of a large number of niche players gives pharma the ability to fully leverage the technology’s benefits through strategic partnerships and co-investment deals. AI penetration in R&D is currently at 25 percent and is expected to grow given its high adoption in Phase 1 and its implications for other areas of pharma. The supply market for AI is highly fragmented with niche suppliers and has just moved from the nascent to the growth stage of the technology adoption curve.
Big Data Analytics (Growth Stage)
The greatest benefit of adopting Big Data technology is it enables decision-making across the value chain from discovery research to the real world. The adoption rate of Big Data within R&D is at 70 percent. Real-world data collected from EHR/EMRs, lab data, genetics data, and trial data, combined with machine learning and artificial intelligence, will be beneficial for architecting the success of clinical trials. The supply market is seeing increased M&As of niche technology providers with the Big Data firms and CROs in the clinical research industry, to form strategic partnerships with pharma by providing end-to-end services.
Blockchain (Nascent Stage)
The integration of blockchain into clinical research studies is still in its infancy; however, the continual collaboration of pharma with blockchain suppliers will enable its application across various aspects of the clinical trial value chain, thereby streamlining the process and providing time, cost, and security benefits. The penetration of blockchain in R&D is at 15 percent, with the supply maturity still at the nascent stage. Startups with highly specialized expertise seem to dominate the market.
Clinical Trial Payments (Growth Stage)
Investment in clinical trial technology in coming years will be mainly directed toward technologies like Big Data and blockchain. Due to high adoption of clinical trial management systems (CTMSs) and mobile payments, suppliers have been able to quickly scale up and mature. Integration across various other technologies and ease of use will be the major factors determining supplier innovation. The current adoption rate is at 80 percent, with the supply market moving toward the maturity stage owing to its increased adoption.
Patient Engagement Solutions (In Growth Stage)
There is growing investment in digital technologies to design patient-centric tools to improve patient engagement. Mobile health, electronic health records, and patient-generated data remain key focuses of patient engagement solutions. The adoption rate of these solutions is at 60 percent, with the increased adoption of customer-centric well-being products. The supply market is in the growth stage, as suppliers are innovating to explore better and more efficient means of engaging patients.
Conclusion
Disruptive technologies like wearables, mHealth, and RWE are paving the way to small, controlled clinical trials. From patient enrollment to drug administration and follow-ups, everything is executed through a phone given to trial participants. Recently, pharma companies have increased spending on AI and Big Data analytics, given their transformative power over the R&D process and cost savings. Fear of competition in the market, in addition to business transformation and agility, are key forces driving huge investments in R&D technologies. Hence, it is essential for pharma companies to identify external innovation through supplier benchmarking in each of these categories and be involved in early engagement through co-developments to stay competitive.
About The Author:
 Mathini Ilancheran is the principal analyst of R&D for Beroe Inc. She specializes in understanding market scenarios and industry dynamics across the globe in the outsourcing arena. Her analysis has enabled global fortune 500+ companies in their strategic decisions on service outsourcing contracts, category management and efficient sourcing. She has written for several publications related to R&D procurement opportunities. With her category knowledge, she has published 25+ articles in leading journals, co-authored with industry experts. She has a master's in management from University College London (UCL) and has worked as a consultant in the U.K. You can contact her at mathini.ilancheran@beroe-inc.com or connect with her on LinkedIn.
Mathini Ilancheran is the principal analyst of R&D for Beroe Inc. She specializes in understanding market scenarios and industry dynamics across the globe in the outsourcing arena. Her analysis has enabled global fortune 500+ companies in their strategic decisions on service outsourcing contracts, category management and efficient sourcing. She has written for several publications related to R&D procurement opportunities. With her category knowledge, she has published 25+ articles in leading journals, co-authored with industry experts. She has a master's in management from University College London (UCL) and has worked as a consultant in the U.K. You can contact her at mathini.ilancheran@beroe-inc.com or connect with her on LinkedIn.

 ment and lack of evidence on patient outcomes
ment and lack of evidence on patient outcomes