A Guide For Managing Decentralized Clinical Trials
In the past several years, decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) have rapidly moved from the margins to the mainstream of clinical research. By reducing or eliminating the need for participants to visit sites, DCTs promise to alleviate the global clinical trial enrollment crisis that leads to costly study delays or even cancellations.
However, DCTs are not a monolith but range from mainly on-site trials with some DCT elements to fully remote trials. Across this spectrum, DCTs leverage technology and remote monitoring techniques to conduct clinical research to reduce participant burden. This comprehensive guide explores the spectrum of DCT options that can improve recruitment, retention, and patient centricity as well as identify best practices and challenges to implementing decentralized trials.
Table Of Contents:
- Why Are DCTs A Growing Trend?
- Benefits Of Decentralized Clinical Trials
- DCT Technology Components And Infrastructure
- Global Regulatory Landscape And Ethical Ethical Concerns For DCTs
- Data Management In Decentralized Clinical Trials
- Quality Assurance And Oversight In DCTs
- Key Challenges In Decentralized Trials
- Real-World Examples Of Decentralized Clinical Trials
- The Future Of Decentralized Trials
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why Are DCTs A Growing Trend?
DCTs aren't a fleeting trend but a response to the pressing challenges faced by conventional trials, particularly patient recruitment, accessibility, diversity, and cost-effectiveness. For example, when study participants are required to make frequent visits to sites, potential candidates, especially those from underserved or remote areas, are reluctant to join a clinical trial. By decentralizing these trials, we not only open doors for a wider, more diverse participant pool but also reimagine a more patient-centric approach to clinical research.
Definition Of Decentralized Clinical Trials
DCTs leverage advanced technologies to conduct some or all trial activities at locations other than traditional clinical sites, such as participants' homes or local healthcare facilities. Telemedicine, mobile healthcare providers, in-home nurses, and digital tools for data collection and communication all reduce the need for in-person visits. DCTs aim to increase participant diversity, improve data quality, and lower costs by minimizing logistical barriers associated with traditional site-based trials.
Traditional Vs. Decentralized Trials: Key Differences
DCTs and traditional, site-based trials differ in several critical areas:
Location And Structure
Traditionally, clinical trials required participants to visit central sites for data collection and interaction with the study team. DCT technologies, however, allow participants to engage from a variety of locations, even their own homes.
Technology Use
All clinical trials rely on technology, but DCTs take the technology a step further by utilizing telemedicine, wearable devices, and electronic data collection to facilitate remote participation.
Participant Diversity And Accessibility
When trials are location-bound, it’s difficult to recruit participants in rural or underserved communities. Diversifying the trial’s location helps diversify its participant population as well.
Data Collection And Management
Typically, trial data is collected during scheduled site visits, but manual collection leaves room for error, and canceled visits can harm study timelines. Continuous data collection through digital tools used in DCTs is more accurate and timelier than in-person methods.
Cost And Efficiency
Sites’ use of physical infrastructure and personnel can create high costs for sponsors. Minimizing the need for physical sites and reducing the size of the investigative team can help sponsors save trial costs.
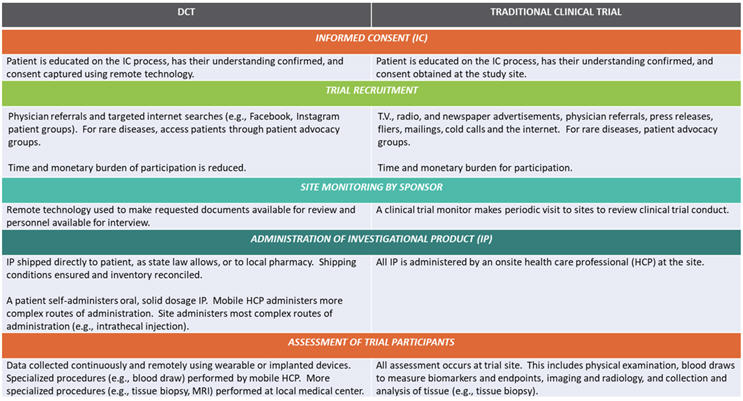
DCTs vs. Traditional Clinical Trials (© Pharmatech Associates – a USP company)
Importance Of DCTs In The Modern Clinical Research Landscape
Given these advantages, DCTs have become increasingly important in modern clinical research. In addition to enhancing diversity and accessibility, DCTs improve data quantity and quality through continuous monitoring and digital health technologies that give timely and accurate information about participants’ real-world experiences. Companies can leverage this information for adaptive trial designs, enabling study teams to respond quickly to data and optimize protocols. As clinical research advances, DCT capabilities are increasingly vital to accelerating drug development and enhancing patient centricity.
Benefits Of Decentralized Clinical Trials
The advantages of DCTs are manifold, weaving together benefits for both researchers and participants alike. DCTs can provide the following benefits:
Enhancing Patient Accessibility And Convenience
One of the biggest advantages of DCTs is their ability to significantly mitigate geographical barriers, making it easier for participants to enroll and partake in trials. This not only increases the diversity of the participant pool, but it can also increase the number of participants enrolled by providing access to those who live in remote areas for whom traveling regularly to a traditional site would be cumbersome or costly.
Improving Cost Efficiency
Traditional clinical trials are often accompanied by high overhead costs, encompassing site expenses, on-ground staff, and travel stipends. DCTs, through their virtual nature, can — depending upon the technology chosen and the training needed for it — reduce these expenses. A thorough cost-benefit analysis should guide the decision-making process when opting for a DCT.
Accelerating Recruitment And Retention Timelines
DCTs aim to accelerate study recruitment by accessing a larger and more diverse participant base. Digital tools and remote monitoring empower participants and boost their engagement, leading to higher retention rates. Similarly, the convenience that DCTs offer patients and caregivers can lower dropout rates compared to conventional trials.
Providing Real-Time Data Collection
Leveraging digital health tools, DCTs facilitate continuous, real-time data collection. Wearables and remote monitoring tools provide a constant influx of patient data, allowing for timely interventions, enhanced safety monitoring, and data-driven insights. Should an adverse event occur, remote monitoring can alert study investigators in real time, allowing for immediate intervention and, when necessary, protocol adjustments. Also, these devices don’t depend on participants’ or caregivers' memories to recall important details related to their health during the study, reducing the amount of incorrect or missing data that could negatively affect the trial.
Examples of digital assessments, endpoints, and biomarkers for clinical trials (Image credit: Sanofi)
DCT Technology Components And Infrastructure
Although digital platforms can be used in traditional trials to deliver information such as a study’s objectives, procedures, and safeguards, technology plays a much larger role in DCTs. Social media campaigns, virtual webinars, interactive apps, and email newsletters are effective tools for maintaining ongoing communication, sharing study updates, and addressing patient queries. Gamified elements, milestone rewards, and regular feedback loops can encourage continuous participation. SMS reminders, interactive challenges, and virtual peer communities can further enhance adherence to study protocols.
But digital doesn't always mean impersonal. Virtual helpdesks, teleconsultations, and chatbots can offer real-time assistance, ensuring participants have a support system whenever they encounter challenges. The following are some of the fundamental technologies that form the backbone of DCTs.
Wearables For Remote Monitoring
DCTs frequently rely on wearables and mobile health devices to collect patient data remotely. From smartwatches that monitor heart rate and sleep patterns to specialized devices that track specific health metrics, these gadgets enable continuous data collection without participant discomfort. When selecting remote devices, it’s important to keep patient needs and preferences in mind to ensure that the device is easy and enjoyable to use.
Telemedicine's Role In DCTs
Essential for remote patient consultations, telemedicine platforms facilitate virtual interactions between researchers and participants. This digital bridge not only keeps communication channels open but also allows for timely interventions, ensuring patient safety and study adherence.
Innovations In Digital Patient-Engagement Tools
Digital engagement tools, like mobile apps and interactive platforms, send reminders, share educational content, and provide a medium for participants to report symptoms or ask questions, fostering a sense of involvement and trust. Also, these platforms can be presented to patients in their native languages for a personalized experience that reduces communication errors.
Data Storage, Backup, And Security Protocols
With the massive amounts of digital data generated by remote devices, DCTs necessitate robust storage solutions. Cloud storage, integrated with strong encryption and cybersecurity measures, ensures data integrity and confidentiality, addressing potential concerns related to data breaches or misuse.
eConsent For Informed Participation
In the clinic, informed consent often is a multi-hour process in which site staff explain all of the risks and benefits to patients. Adopting eConsent platforms frees up site staff’s valuable time and tools such as videos and interactive quizzes, which can be tailored to participants’ native language, enhance patient understanding.
Although eConsent can be used for any type of trial, the digital realm of DCTs requires this approach to informed consent. In DCTs, eConsent platforms facilitate the remote delivery, comprehension, and acknowledgment of study information. These platforms prioritize clarity and ensure participants are fully aware of study implications.
Global Regulatory Landscape And Ethical Ethical Concerns For DCTs
As DCTs gain traction, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting their guidelines to encompass this new model. The appearance of new and emerging DCT technologies has driven regulatory initiatives and serious concerns about data privacy and security. Sponsors conducting trials in multiple countries must stay informed about country or region-specific regulations and seek guidance from regulatory experts to ensure compliance.
DCT Regulations In Important Countries And Regions
United States
The FDA released draft guidance in May 2023 to address implementation, patient safety, and data integrity for DCTs and launched the Digital Health Center of Excellence to advance digital health technologies in clinical trials.
Canada
Health Canada has issued regulatory proposals to enable and encourage DCTs, including a clinical trial regulatory modernization initiative
European Union
The EMA issued a recommendation paper on DCTs in 2022, emphasizing patient safety and data integrity. Individual European countries, such as Denmark and Sweden, have established their own regulatory frameworks for DCTs.
United Kingdom
The Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency has released guidance on managing clinical trials during the pandemic, which includes considerations for DCT.
APAC
The APAC region is a promising frontier for DCTs, with countries like Singapore and China issuing guidance on clinical trials that incorporate decentralized elements.
Ethical Considerations In Decentralized Trials
In conjunction with regulatory changes, the increased prevalence of DCTs has prompted some ethical concerns. For example, eConsent, which is especially useful for a DCT, must still uphold the principles of traditional informed consent. Thus, an eConsent platform should not only ensure participant comprehension (e.g., via interactive modules, videos, and quizzes), but it must also provide an easy way for patients to contact study personnel for clarifications.
Another ethical consideration is that DCTs may unintentionally exclude those without access to technology or digital literacy. In those instances, efforts must be made to provide necessary resources (e.g., Wi-Fi) or alternative participation methods, such as providing home nurses to record participant data. Furthermore, a lack of in-person oversight can lead to greater risks to patient safety and rights. Rigorous ethical controls are needed to protect patients throughout the trial.
Data Management In Decentralized Clinical Trials
Similar to regulatory and ethical concerns, the potential for broader decentralized data collection, such as continuous monitoring, raises questions about patient privacy and data security. It’s imperative to develop robust encryption, secure data storage solutions, and clear data-handling policies. Of course, study participants should always be informed (via the informed consent document) about who can access their data and for what purposes. A successful DCT incorporates sophisticated data management platforms and plans for the following:
Leveraging Advanced Data-Collection Tools
In DCTs, data collection extends beyond the traditional patient-reported outcomes. Ensuring the reliability and accuracy of these tools is paramount to maintaining data quality. Additionally, companies must ensure that the devices they choose are compliant with local regulatory authorities. Common data collection tools include:
- Electronic patient-reported outcomes (ePRO) enable patients to self-report their experiences and symptoms.
- Wearable devices like sensors and smartwatches continuously monitor vital signs and activity levels.
- Mobile health/ smartphone apps are designed for data input and communication with the research team.
- Telemedicine platforms provide video conferencing tools for virtual visits and remote consultations.
- Electronic diaries allow patients to record daily observations and experiences.
- Remote monitoring devices measure specific health parameters at home.
- Electronic case report forms (eCRFs) are used by investigators to input clinical data.
Integrating And Harmonizing Data
Harmonization normalizes data collected from various sources to ensure compatibility and comparability. Variables are mapped and standardized across trials using a single data model that defines their formats and allowed values.
Standardized data processing pipelines manage differences in data collection and analysis methods so that data from different sources is processed uniformly, enhancing comparability. The data is stored in centralized electronic systems to facilitate data collection, compliance, and harmonization efforts by providing a consistent platform for managing trial documentation.
Rigorous data quality checks and cleansing processes identify and resolve inconsistencies, ensuring the integrated dataset’s integrity. Finally, liaising with ethics committees, regulatory bodies, and data governance organizations ensures compliance with ethical and regulatory requirements while harmonizing data from various sources.
Ensuring Data Integrity And Security
The remote nature of DCTs brings forth concerns about data tampering or misrepresentation. Implementing real-time data validation and verification protocols backed by blockchain or similar technologies can enhance trust in the collected data. Robust cloud storage solutions with strong encryption and cybersecurity measures are essential. Regular data audits, both automated and manual, also reinforce integrity. Clear data access and sharing policies protect patient confidentiality, and companies should use centralized statistical monitoring and automation to detect anomalies. Training personnel on DCT-specific standard operating procedures and maintaining comprehensive audit trails further enhance data integrity and security.
Strategizing Data Storage And Retrieval
Cloud storage solutions, equipped with robust encryption, offer scalable and secure storage options for DCTs. Regular backups and redundancy plans are essential to prevent data loss. Data partitioning and compression optimize storage space and access speed, while caching frequently accessed data improves retrieval efficiency.
Controlling Access To Sensitive Data
Clearly defined policies should be in place regarding who can access the data, under what circumstances, and for what purpose. Comprehensive solutions include robust multifactor authentication, sophisticated access control models like RBAC and ABAC, and advanced encryption techniques. Centralized identity and access management (IAM) platforms dynamically manage user permissions, ensuring participants and researchers access only necessary data. Regular security audits help monitor access patterns, detect potential vulnerabilities, and maintain compliance with stringent healthcare data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA, ultimately safeguarding sensitive clinical trial information.
Extracting Analytics And Actionable Insights
The vast amount of data generated in DCTs holds untapped potential for insights. Advanced analytical tools powered by AI and machine learning can sift through the data, identifying patterns, predicting patient outcomes, and offering actionable insights for researchers.
For example, data visualization transforms complex data into intuitive graphics, and ML algorithms identify patterns and trends. Centralized platforms for data integration harmonize diverse data sources, while real-time analytics enable timely interventions and decision-making.
Quality Assurance And Oversight In DCTs
QA and oversight are fundamental to the success of any clinical trial, but in the context of DCTs, they assume even greater significance due to the inherent challenges of the model.
DCTs largely rely on digital platforms, wearable devices, and remote interactions, so a multifaceted QA system is crucial. This system should be agile, capable of evolving in tandem with technological advancements, and patient-centered to ensure all touchpoints are governed by quality standards. For example, any remote monitoring tools used with a DCT should be able to verify data integrity in real time, detect anomalies, and alert researchers to potential discrepancies or concerns.
Establishing Standard Operating Procedures For DCTs
While the core principles of clinical research remain unchanged, DCTs necessitate SOPs tailored to their unique requirements. These SOPs should address areas such as informed consent, remote adverse event reporting, and data security measures.
Providing Training And Certification
Ensuring that all personnel involved in the DCT are well-versed with its nuances is crucial. Regular training sessions, certifications, and refresher courses can ensure that the trial is conducted to the highest standards, regardless of the decentralized model.
Conducting Data Audits
Regular and random audits of the collected data can reinforce its integrity. Automated audit trails, coupled with manual reviews, can provide a holistic view of the trial's quality parameters. In particular, for DCTs, these audits verify data from disparate sources like wearables, ePROs, and remote monitoring tools to ensure consistency and regulatory compliance. They also identify potential fraudulent data or misconduct, which can be challenging to detect in decentralized settings.
Creating Risk Management And Contingency Plans
Proactively identifying potential risks — be it technological glitches, patient non-compliance, or data breaches — and having contingency plans in place can ensure swift resolution while maintaining the trial's integrity. Risk management also includes alerting researchers to potential safety issues; for example, if a wearable device records a sudden drop in a participant's heart rate, the information should be immediately sent to the PI and flagged as "high priority." Although this adds an extra layer of contingency planning to DCT design, real-time participant data can improve safety.
Gaining Stakeholder Collaboration For Oversight
Regular reviews and consultations with stakeholders, including patients, can offer a comprehensive perspective on the trial's quality. Transparent communication and a commitment to continuous improvement can further bolster QA.
Adhering To Regulatory Guidelines
Aligning with regulatory guidelines is not just a compliance requisite but also a cornerstone of quality. Regular updates, documentation, and ensuring that DCTs adhere to both local and international regulations are paramount.
Key Challenges In Decentralized Trials
Despite DCTs’ many advantages, adopting DCT methodologies comes with hurdles and constraints. For instance, clinical trial sites may struggle to manage DCTs.
Solutions To Overcome Technological And Accessibility Barriers
First, companies should work to provide the necessary equipment to participants to ensure equal access. However, simply providing the technology is not enough to cross the technological divide. Technical support and training for patients and caregivers is vital to keeping patients engaged throughout the study. Selecting user-friendly interfaces and adaptive technologies helps reduce the learning curve. Regular user testing and accessibility audits will help companies solve problems before they delay studies.
Strategies For Remote Patient Adherence And Engagement
With less physical oversight than traditional clinical trials, it’s harder to ensure make sure that participants adhere to trial protocols or take prescribed medications. So, too, is maintaining clear, consistent, and immediate communication with participants to avoid potential misunderstandings or reduced patient engagement.
While the remote nature of a DCT has its advantages, less face-to-face interaction can make some participants feel detached, which can influence their experience and, in some cases, their commitment to the trial. Likewise, DCTs' globalization opportunities provide a more diverse pool of patients but introduce complexities like cultural differences or language barriers that can hinder engagement.
Interactive apps, virtual webinars, and social media campaigns help maintain communication between researchers and patients. Gamified elements and milestone rewards encourage participation, while SMS reminders and online peer communities help reinforce protocol adherence. Virtual resources such as helpdesks, teleconsultations, and chatbots offer users real-time assistance.
Mitigations For Privacy Risks And Enhanced Data Security Across Platforms
Robust encryption for data transmission and storage, multifactor authentication, and role-based access control help safeguard sensitive data. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments let companies know if they are at risk of a data breach. IAM platforms and regulatory compliance are also key to reducing risk. However, additional technology can add to site staff’s already crowded workflows and thus must be chosen carefully.
Finally, not every study is ideally suited to be conducted via DCTs. Trials requiring intensive medical procedures, frequent physical assessments, or specialized equipment might be more efficiently managed in traditional settings.
Real-World Examples Of Decentralized Clinical Trials
To truly grasp the potential and efficacy of DCTs, it's invaluable to examine real-world examples. Currently, many trials are using DCT elements, and below are notable examples of completed and ongoing trials who successfully navigated the challenges, demonstrating the positive impact of this innovative research approach.
Pfizer’s REMOTE Trial
- Background: In 2011, Pfizer launched the first-ever fully remote clinical trial, the REMOTE (Research on Electronic Monitoring of Overactive bladder Treatment Experience) trial, aimed at studying overactive bladder condition. While the trial faced challenges like recruitment difficulties and was eventually terminated, it paved the way for further exploration and understanding of decentralized methodologies.
- Approach: Patients used mobile apps and online platforms for everything from recruitment to data collection. They also received investigational drugs by mail.
Advicenne ARENA2 Trial
- Background: Began recruiting for the rare kidney disease trial in 2019 but was put on hold when COVID-19 hit. The original design required patients to go through a six-day withdrawal period after receiving the active drug or placebo in a hospital setting.
- Approach: Blood draws previously conducted in clinics were performed by nurses in patients’ homes. Patients could record outcomes they experienced and schedule appointments using an app/platform, and there would be telemedicine calls with the doctor.
Janssen CHIEF-HF Trial
- Background: Included 448 randomized patients recruited between March 2020 and February 2021. CHIEF-HF stands for Canagliflozin: Impact on Health Status, Quality of Life and Functional Status in Heart Failure. The study demonstrated that canagliflozin resulted in a rapid and clinically meaningful improvement in the symptoms of patients with HF.
- Approach: Designed to have no in-person site visits, participants were given their study medication and a Fitbit and completed an eDiary of medication use. Ninety-five percent of participants completed their eDiary and 91% took more than 80% of their medication.
Johns Hopkins University REACT-AF
- Background: Rhythm Evaluation for AntiCoagulaTion with Continuous Monitoring of Atrial Fibrillation (REACT-AF) launched in July 2023 and is expected to run through July 2029. This large, pragmatic study of over 5,000 participants is testing an alternative anticoagulation therapy for patients with atrial fibrillation (AF).
- Approach: This hybrid trial incorporates decentralized elements, which is expected to improve data collection while decreasing trial costs by 50%. After enrollment, no in-person follow up visits are required, and participants use an Apple Watch to collect data remotely.
The National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) PREVENTABLE
- Background: PRagmatic EValuation of EvENTs And Benefits of Lipid-Lowering in OldEr Adults (PREVENTABLE) is a hybrid trial utilizing pragmatic data sources for a target sample size of 20,000 participants.
- Approach: The trial uses randomized evidence to determine whether statins reduce cognitive and functional decline in older adults. Recruitment completed in April 2023, and the trial will conclude in 2026. As a hybrid trial, participants are required to visit sites for period blood draws and performance tests, but visits are supplemented with a call center that performs annual assessments.
The Future Of Decentralized Trials
DCTs represent a paradigm shift in clinical research. By prioritizing patient convenience, embracing technology, and optimizing costs, they herald a more inclusive, efficient, and data-rich future for clinical trials, underlining the potential to revolutionize the way medical research is conducted.
Why Are DCTs Becoming More Popular?
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of DCTs, demonstrating their potential to maintain research continuity during global disruptions. Since then, a growing number of pharmaceutical companies, biotechs, and research institutions have adopted decentralized methodologies, and this trend is expected to increase significantly. Recruitment potential plays a significant role in their growing popularity, as the number of trials that fail due to lack of enrollment is staggering. Thus, methods that make trials more attractive to participants offer distinct advantages.
What Is The Role of Emerging Technologies?
Emerging technologies play a crucial role in enabling and enhancing DCTs. For example, wearable devices and sensors provide continuous, real-time health data collection, while telehealth platforms offer remote consultations between researchers and participants. AI and ML are being used to improve patient enrollment and recruitment, and blockchain technology is emerging as a secure method for managing participant consent and data sharing.
How Are Regulatory Guidelines Evolving?
As DCTs gain momentum, global regulatory bodies are refining and expanding guidelines tailored to decentralized methodologies. Most importantly, regulatory authorities want to ensure that DCTs maintain rigorous standards of safety and efficacy while recognizing the advantages of remote participation. The FDA, EMA, and other agencies are working on improving their guidance to ensure that innovation in clinical trials translates into better health outcomes.
Hybrid Trials
Hybrid trials combine elements of traditional site-based trials with decentralized components, offering flexibility to both participants and researchers. This balanced approach allows for the integration of DCT methodologies while maintaining some aspects of conventional trials. Hybrid models can be tailored to specific study needs, potentially incorporating in-person visits for critical assessments while leveraging remote technologies for routine data collection and follow-ups.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
DCTs are complex, and companies considering implementing a hybrid or remote trial often ask the following questions before proceeding:
1. What is a decentralized clinical trial?
A decentralized clinical trial is a study that uses technology and innovative methods to bring trial activities directly to participants, reducing or eliminating the need for them to travel to centralized research sites. DCTs may involve telemedicine, wearable devices, mobile health apps, and home visits to collect data and monitor participants remotely.
2. What is the difference between centralized and decentralized procedures?
In the context of clinical trials, a centralized procedure involves conducting all trial activities at designated research sites, while a decentralized procedure distributes these activities across various locations, including participants' homes, using technology and remote methods. Decentralized procedures offer greater flexibility and accessibility but may require more complex coordination and data management.
3. Why are DCTs and DHTs becoming a larger component of the clinical trial landscape?
DCTs and digital health technologies (DHTs) are becoming more prominent in clinical trials due to:
- Advancements in technology enable remote data collection and monitoring.
- Increasing focus on patient-centricity in healthcare and research
- Need for more efficient and cost-effective clinical trial methods
- Growing acceptance of telemedicine and remote healthcare practices
- Desire to increase diversity and representativeness in clinical research.
4. What is the difference between a decentralized, virtual, hybrid, or remote clinical trial?
While these terms are often used interchangeably, there are differences:
- Decentralized trials: Broadly refers to trials that move activities away from centralized sites to participants' locations.
- Virtual trials: Typically involve conducting the entire trial online without any in-person interactions.
- Hybrid trials: Combine elements of traditional site-based trials with decentralized components.
- Remote trials: Generally, refers to any trial conducted away from a centralized research site, which could include decentralized, virtual, or hybrid approaches.
5. What Are DCTs’ advantages?
DCTs offer several benefits:
- Increased patient participation and broader recruitment
- Enhanced patient experience and convenience, leading to improved retention rates.
- Real-time data collection through technology-enabled solutions, improving data accuracy and timeliness.
- Faster startup times due to reduced need for physical research sites
- Cost-effectiveness by minimizing travel expenses and physical infrastructure requirements.
- Improved data quality through electronic data capture systems and standardized protocols
- Increased diversity and representativeness in study populations
6. What are DCTs’ disadvantages?
Some potential drawbacks of DCTs include:
- Potential technological barriers for some participants
- Difficulty in standardizing procedures across different home environments
- Potential privacy and security risks associated with increased digital data collection.
- Regulatory uncertainties in some regions regarding the acceptance of DCT data
- Challenges in ensuring data integrity and quality across diverse remote settings.
- Difficulties in standardizing data formats and protocols across different platforms
7. How do DCTs ensure data security and compliance?
DCTs ensure data security and compliance by
- Implementing robust encryption for data transmission and storage
- Using multifactor authentication and role-based access control
- Conducting regular security audits and vulnerability assessments
- Employing centralized IAM platforms
- Ensuring compliance with healthcare data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA
- Implementing quality procedures for data collection processes and documentation
- Adapting traditional risk management activities to include IT system audits
- Utilizing centralized data analysis platforms to monitor risks and enable compliance.
8. What technologies do DCTs use?
DCTs utilize various technologies, including:
- Telemedicine platforms
- Wearable devices and sensors
- Mobile health applications
- ePRO systems
- eConsent platforms
- Remote monitoring devices
- eCRFs for clinical data input
- Cloud-based data storage and management systems
- Data analytics and visualization tools
9. What are the best practices for DCT patient recruitment?
Best practices include:
- Leveraging social media and digital marketing
- Implementing user-friendly interfaces and adaptive technologies
- Providing necessary equipment and ongoing technical support to participants and caregivers
- Offering virtual information sessions and webinars to educate potential participants
- Utilizing patient advocacy groups and online communities to spread awareness
- Implementing flexible scheduling options
- Ensuring clear communication about the trial process and expectations
- Emphasizing the convenience and reduced burden of participation in DCTs
10. Are DCTs the future of clinical research?
DCTs are considered by many to be the future of clinical research because they address many limitations of traditional trials. They increase accessibility, diversity, and representativeness in study populations, potentially leading to more generalizable results. DCTs also align with the growing trend of patient-centricity in healthcare, leveraging technology to make participation more convenient and less burdensome for patients.
Additional Resource:
The Decentralized Trials Research Alliance (DTRA) resource library provides a comprehensive collection of DTRA content supporting the adoption of DCTs.
About The Author
Elizabeth Mann is a skilled writer with over a decade of experience in content creation, specializing in the life sciences industry. As a writer for Life Science Connect, she develops in-depth content that informs and engages professionals in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device sectors. Her areas of focus include biologic drug production (including cell and gene therapies), clinical trial design and execution, and drug development and manufacturing outsourcing.
FREE DCT E-BOOK

This free e-book from Clinical Leader explores the ongoing adoption of decentralized trials, the challenges companies face in implementing DCTs, and the promise they hold to reduce the time and cost of conducting trials. Download it today!
EXPERT INSIGHTS ON DECENTRALIZED TRIALS
-
Clinical Supply's Role In Driving Success In Decentralized Trials
Decentralized trials are a challenge for supply chain professionals. Explore how logistics, labeling, and home delivery make or break trial outcomes.
-
Trends In Rare Disease Trials: Recommendations
In the third article of this series, analyst reveal their top 6 recommendations for designing selection criteria and selecting solution options to optimize rare disease research outcomes.
-
What The FDA Says About Investigator Responsibilities In DCTs
Learn exactly what the FDA says about the use of healthcare providers (HCPs), telemedicine, licensing, and practice standard requirements when executing a DCT.
-
Bridging Community And Central Hospitals With Japan's DCT Model
Regulatory support and improved DCT infrastructure, as well as a uniquely Japanese approach to site relationships, are advancing the DCT landscape in Japan, explains consultant Takuma Matsunaga.
-
CISCRP's Mobile Health Exhibit Brings Clinical Trial Education To Communities
CISCRP shares its mobile education project brings clinical trial awareness and information directly to communities.
EDITORIAL PERSPECTIVES ON DECENTRALIZED TRIALS
-
DCT Benefits Are Proven, Yet Progress Is Slow
Despite the clear benefits of decentralized trials—broader reach, better retention, and higher diversity—adoption has been slow. In this interview, Sunny Kumar of Informed Ventures explains how AI is lowering costs, speeding up study builds, and pushing DCTs from fringe to future.
-
Tufts & PACT Release New DCT Analysis
We take a closer look at some of the key stats in a new DCT report from the Partnership for Advancing Clinical Trials (PACT), a consortium hosted and facilitated by the Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development (CSDD).
-
Local HCPs In DCTs: A Game-Changer For Oncology Trials
An AMC’s decentralized trial model uses local HCPs to expand oncology research access across North Carolina while maintaining regulatory compliance and building on early DCT experiences and FDA collaboration.
-
7 Steps To Manage Local HCPs In A Decentralized Trial
Here’s a template you can use for a multi-step process to create a centralized system to verify the credentials, licenses, and professional standing of all local healthcare professionals (HCPs) participating in a DCT.
-
Local HCPs in DCTs: Big Benefits, Bigger Burdens?
Local HCPs in DCTs provide benefits like improved patient accessibility, retention, and diversity, but create significant oversight burdens for investigators and sponsors, requiring extensive documentation, training protocols, and communication systems to maintain compliance.
ON-DEMAND DCT WEBINARS
-
Real-World DHT Adherence Insights And Good Practices
While advances in sensors and device design are improving wearability, successful data collection still hinges on participant adherence. The session highlights why addressing this can’t be an afterthought.
-
Inspection Readiness For Decentralized Trials
Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) enhance research inclusivity by minimizing logistical barriers such as travel, scheduling conflicts, and costs, making participation more accessible.
-
A Framework For Selecting Reliable Clinical Endpoints From Real-World DHT Data
Dr. Andy Liu presents a case study determining which digital measure of physical activity would be a well-defined and reliable clinical endpoint in a trial including patients with diabetes.
-
Digital Physical Activity Measures In Phase 3 Immunology Trials
Dr. Jie Shen, Research Fellow and Director of Digital Science at AbbVie, shares lessons learned from incorporating digital measures of physical activity into Phase 3 immunology clinical trials.
-
Leveraging DHTs To Improve Data Collection And Analysis
How can wearable DHTs be leveraged to measure physical activity in patients with immunological diseases, enhancing clinical trials and advancing drug development?
















