Consolidation In The Core Lab Market — What Pharma Companies Need To Know
By Samiya Luthfia Khaleel,lead analyst, Clinical R&D, Beroe Inc.

Clinical laboratory services are the most outsourced services by pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, and medical device companies. Trending in the central or core laboratory services market is consolidation and integration of services through acquisitions and collaborations inorganically to expand beyond core services. Through horizontal integration suppliers increase their market share.
What is a core laboratory? Core laboratories collect, process, and analyze data (electrocardiography [ECG], imaging, or spirometry) from multi-center clinical studies through a single platform to prevent inter- and intra-variability by following standardized protocols. Unified and standardized data collection with stern quality control methods facilitates easy central review by physicians and reduction in errors and meets expectations and approval of regulatory authorities.
Why Is There A Need For Consolidation Among Service Providers?
The primary reason for consolidation is to meet the increasing demand of clients. Companies are adding multiple capabilities to their service portfolios to give a one-stop shop solution to their clients. Clients, on the other hand, can be less concerned about data loss during transfer because service providers can collect and analyze multiple data sources from multiple modalities.
The recent consolidation in the core lab space actually reinforces the need for specialized and experienced core labs. As core labs consolidate and become larger, there is an increasing need for niche providers with a high level of experience and expertise for specific trials. Large pharma companies usually outsource core lab operations to two to three preferred providers. And, there is a trend of more project-based outsourcing from pharma companies, which implies engagement in a transactional business to leverage the service provider’s niche offering in a specific therapeutic area. Value is added to these services through consolidation by acquisition and collaboration to respond to pharma companies ’inordinate demands.

If you are outsourcing core lab services, understanding the Good Laboratory Practices regulations the core lab should follow is critical to developing successful products. Get a clear overview in the course:
An Introduction to Good Laboratory Practices (GLP)
Suppliers’ Consolidation Trends
Core lab service providers are combining their businesses that have been closely integrated partners for years. For example, nSpire Health and iCardiac Technologies Inc. partnered for clinical trials for over five years. Providers may add a new service line or strengthen or expand existing offerings: ERT recently added imaging services to its portfolio by the acquisition of ImageIQ, making ERT a complete core lab service provider. iCardiac Technologies acquired the clinical trials division of nSpire Health to add respiratory and electronic patient-reported outcomes (ePRO) services. Most core lab service providers are moving toward strengthening wireless medical technology — mobile health and biosensors in clinical trials. Examples include ERT, Bioclinica, and BioTelemetry.
Table 1: Core Lab Service Providers Acquisitions
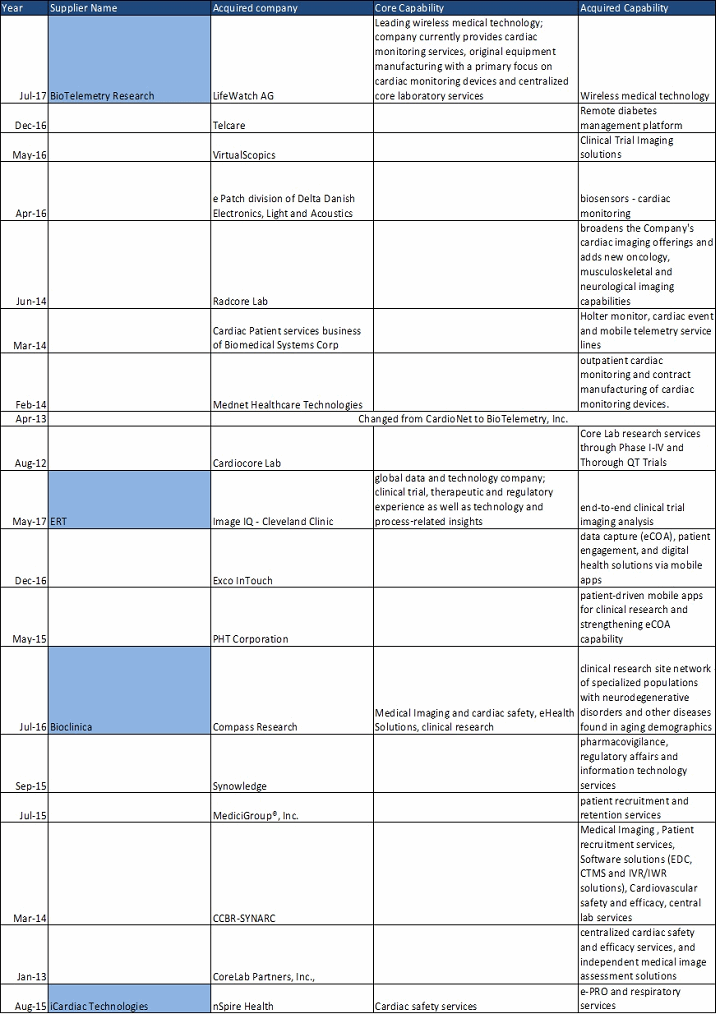
Consolidation has created competition among suppliers in terms of technological upgrades, short project delivery times, improved quality of services, and ability to provide multiple services. With pharma companies wanting to curb their drug development time and costs, the focus on speed to market is high. Large pharma companies completely outsource core laboratory services, and their strategy is to award their work to suppliers that have integrated services like spirometry, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, ECG, electronic clinical outcome assessments, interactive voice response systems, and imaging.
Impact Of Consolidation On Buyers
A consolidated core lab business providing integrated services to its customers leads to cost savings through optimizing project costs, streamlining the project focus, non-duplication of services, increasing productivity, innovative service offerings, providing scalability to customers, additional geographic presence, better asset utilization and optimization, and improved business decisions.
In a different scenario, if a customer’s ongoing project with the acquired company is in the stage where the acquisition takes place, the change and transition poses a challenge to the customer. Early solution design can enable the project course and delivery to remain on time. Any strategy devised by the customer should always pertain to the service provider they are engaged with at that point. Sudden disruption in a relationship may have a negative impact on the project.
About the Author:
 Samiya Luthfia Khaleel is the lead analyst, clinical R&D of central and core lab services procurement, at Beroe Inc. Her role involves regular interaction and networking with more than 100 clinical suppliers and keeping track of market innovations related to the procurement of R&D services. Khaleel completed her master's in biomedical sciences at Aston University, conducting her thesis on asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treatments. She previously worked as a drug discovery scientist and an industrial biotech engineer.
Samiya Luthfia Khaleel is the lead analyst, clinical R&D of central and core lab services procurement, at Beroe Inc. Her role involves regular interaction and networking with more than 100 clinical suppliers and keeping track of market innovations related to the procurement of R&D services. Khaleel completed her master's in biomedical sciences at Aston University, conducting her thesis on asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treatments. She previously worked as a drug discovery scientist and an industrial biotech engineer.
