Elutriation: How It Works

Our counterflow centrifugation system operates on the principle of elutriation. Elutriation is a process for separating cells based on their size, shape and density. Discover the four stages in the lymphocyte elutriation process.
What is elutriation?
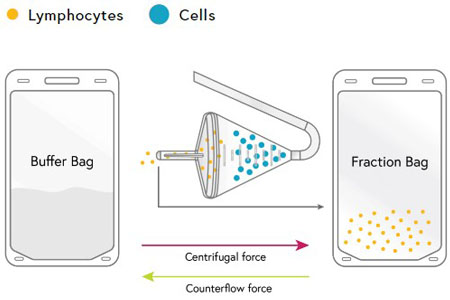
The Korus™ counterflow centrifugation system operates on the principle of elutriation. Elutriation is a process for separating cells based on their size, shape and density using a stream of fluid flowing in the opposite direction to the centrifugal force.
The benefits of elutriation are:
- Separation of target from non-target cells
- Gentle production of a non-pelleting cell bed
Monocyte elutriation
Up to 88.6% monocyte purity and 75.0% recovery. Isolation of monocytes for downstream processes such as dendritic cell (DC) maturation.
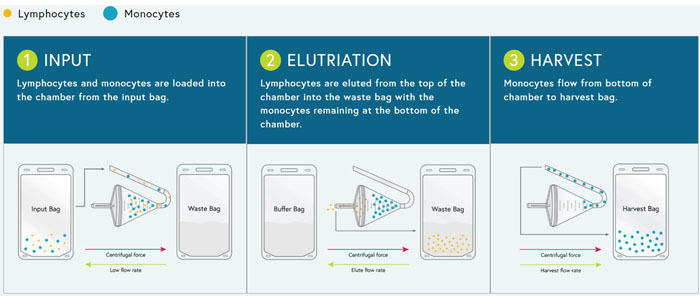
Lymphocyte elutriation
Up to 85.2% lymphocyte recovery and 90.3% purity, providing a cleaner starting material for CAR-T or TIL manufacturing.

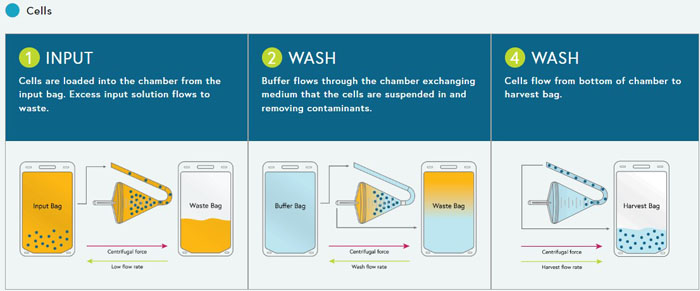
Cell wash
Maximizing cell recovery and contaminant removal.
Manufacturing processes
-
Loading: Transfer of input cells into chamber(s).
![]()
-
Transfer fraction: Transfer of lymphocytes from fraction bag to chamber for concentration.
-
Elutriation: Increased counterflow removes smaller cells (lymphocytes) from chamber(s) to fraction bag.
-
Harvest: Transfer of cells from chamber to harvest bag in a user-defined volume.