Glaucoma: Asia Pacific Clinical Trial Landscape
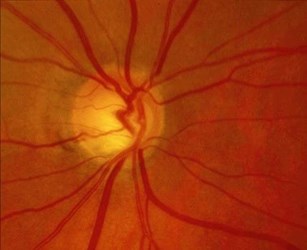
The world is heavily burdened by glaucoma, which is the second-leading cause of blindness and the primary cause of irreversible blindness. (1) Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions caused by injury to the optic nerve brought on by elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) and eventually the loss of retinal ganglion cells. It is one of the most common causes of permanent blindness in the world. (2) The most important risk factor for glaucoma is elevated IOP, while the others include age and frailty, gender, myopia, genetics, family history, smoking, race, systemic hypotension and hypertension, vasospasm, use of systemic or topical drugs, migraine, obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome, and myopia. (3) There are mainly two subtypes of glaucoma: primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) and primary angle closure glaucoma (PACG). The most prevalent glaucoma subtype is primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG). Africa has the highest POAG prevalence (4.2%) while Asia has the highest PACG prevalence (1.1%). (4) The prevalence of POAG increases with age, ranging from 1.1% at age of 40-49 to 9.2% at the age over 80. Males are 36% more likely than females to have POAG. (1).
Get unlimited access to:
Enter your credentials below to log in. Not yet a member of Clinical Leader? Subscribe today.
