Making Rare Disease Progress With Novel Strategies, Data Standardization And More
By Jeff Parke

Research into rare diseases faces unique obstacles, primarily because of the limited number of affected individuals and the diverse nature of these conditions. It's crucial, therefore, to pioneer and apply novel methodological and statistical strategies tailored to navigate these complexities effectively. The expansion of clinical trial networks into multicenter and multinational domains is pivotal for surmounting recruitment hurdles inherent in rare disease research. This global collaboration not only diversifies the genetic and phenotypic landscape of study cohorts but also accelerates the pace of clinical trials, promising swifter transitions from bench to bedside.
One such methodological and statistical strategy to have been recently adopted and recognized for its ability to evolve during the research process is adaptive trial design. This adaptability, rooted in sophisticated statistical techniques, enhances the efficiency of trials and increases the chances of discovering effective treatments. This approach alone represents a larger shift toward research methods that are more attuned to patient needs, significantly improving the development of treatments and patient health outcomes.
Data Standardization And Utilization Bridges Gap Between Data Silos
The integration and standardization of data across disparate sources, facilitated by frameworks such as SNOMED CT and the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO), are instrumental in consolidating the fragmented landscape of rare diseases data. This harmonization supports the effective use of electronic health records (EHR) to precisely identify patient cohorts and streamline the audit of clinical outcomes. The impact of these efforts extends beyond operational efficiency by also fostering an environment in which data-driven insights inform the development of targeted interventions.
Furthermore, the adoption of standardized data formats and common data elements across research endeavors enhances data interoperability, a critical factor in enabling meta-analyses that can unearth novel disease correlations and genetic markers. This systematic approach to data management not only accelerates the trajectory of rare diseases research but also underpins the delivery of personalized medicine, tailoring therapies to the unique genetic and phenotypic profiles of patients.
Deepening Data Integration For Comprehensive Insights
The amalgamation of data through SNOMED CT and HPO extends beyond mere terminological alignment. It encompasses a holistic approach to patient data, capturing a vast array of clinical observations, laboratory results, and patient histories in a structured, interoperable format. This depth of data integration facilitates a more nuanced understanding of rare diseases, enabling researchers to draw correlations between disparate data points that were previously obscured. The precision in data categorization afforded by these ontologies enhances the specificity of research queries, yielding results that are both rich in detail and broad in scope.
Enhancing Clinical Decision Support Systems
The harmonization of data is instrumental in advancing Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS), sophisticated tools that offer evidence-based guidance to healthcare professionals. CDSS leverages standardized data to provide tailored recommendations for diagnosis and treatment, particularly valuable in the complex landscape of rare diseases. By integrating genetic insights with clinical data, these systems offer personalized medicine approaches, considering each patient's unique genetic profile. This integration not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also ensures treatment plans align with the latest research findings, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Facilitating Global Collaboration And Data Sharing
Standardized data formats and common data elements lay the groundwork for global collaboration in the rare disease domain by eliminating the "language barriers" that historically impeded data sharing between institutions and countries. This collaborative approach widens the pool of knowledge and fosters international research initiatives, enabling the identification of epidemiological trends, understanding of genetic variations across populations, and development of interventions with universal applicability.
Achieving efficiency improvements is paramount to advancing scientific endeavors and overcoming the inherent challenges posed by limited data availability and dispersed research efforts. Research efficiency improvement refers to the strategic implementation of streamlined processes and standardized methodologies aimed at optimizing data management, facilitating collaboration, and expediting scientific discoveries.
In practical terms, this involves adopting standardized data formats and common data elements across research projects and institutions. By doing so, researchers can minimize redundant efforts, harmonize data collection and analysis practices, and promote seamless data sharing initiatives. This standardized approach not only accelerates the pace of research but also enhances the quality and reliability of findings by ensuring consistency and comparability across studies.
For rare diseases, where data scarcity and fragmentation are common hurdles, research efficiency improvements play a transformative role. They enable researchers to maximize the utility of available data, leverage collective insights from diverse sources, and uncover novel insights into disease mechanisms, treatments, and patient outcomes.
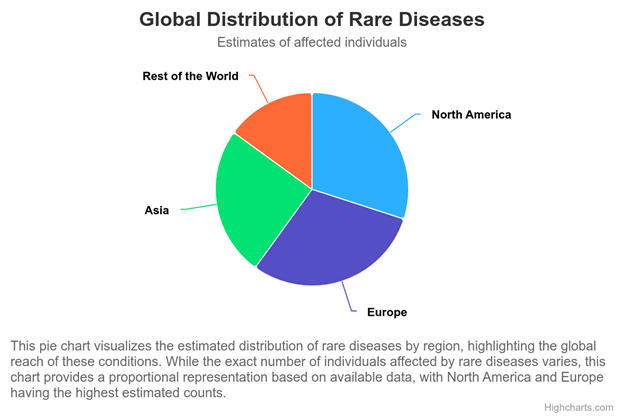
The Orphanet report on the prevalence and incidence of rare diseases is a testament to the power of standardization, offering a repository of data that has likely informed the estimations of affected individuals in regions as illustrated in the pie chart. This reflects the tangible benefits of adopting standardized data formats and common data elements across research projects and institutions.
In practical terms, this involves adopting standardized data formats and common data elements across research projects and institutions. By doing so, researchers can minimize redundant efforts, harmonize data collection and analysis practices, and promote seamless data sharing initiatives. This standardized approach not only accelerates the pace of research but also enhances the quality and reliability of findings by ensuring consistency and comparability across studies.
For rare diseases, where data scarcity and fragmentation are common hurdles, research efficiency improvements play a transformative role. They enable researchers to maximize the utility of available data, leverage collective insights from diverse sources, and uncover novel insights into disease mechanisms, treatments, and patient outcomes. Incorporating the findings from these varied yet standardized data sources allows for a richer, more accurate depiction of the global distribution of rare diseases, as represented in the pie chart and underlines the critical role of international cooperation in rare disease research.
Global data sharing in the context of rare disease research is occurring on a significant scale, with researchers, institutions, and organizations worldwide actively participating in collaborative efforts. However, there are still challenges hindering its full potential, including variations in data formats, privacy concerns, and regulatory barriers. To improve global data sharing, initiatives focusing on standardizing data formats, enhancing interoperability between systems, implementing robust data governance frameworks, and fostering transparent data-sharing agreements are essential. Additionally, promoting a culture of collaboration, incentivizing data sharing, and leveraging emerging technologies can further enhance the efficiency and impact of global data-sharing initiatives.
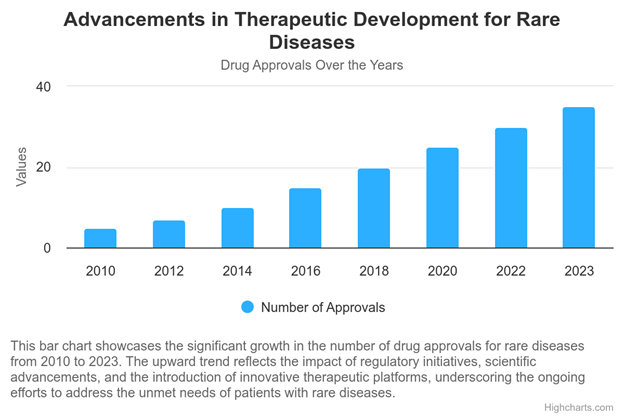
Driving Innovations In Therapeutic Development
Drug discovery processes benefit from an enriched understanding of disease mechanisms, informed by comprehensive data sets that cover genetic, phenotypic, and environmental factors. This integrated perspective is crucial for identifying novel drug targets and repurposing existing therapies to treat rare diseases. Furthermore, clarity and consistency in data reporting facilitate regulatory processes, streamlining the path from laboratory discovery to clinical application.
Integration and standardization of data are not merely technical endeavors; they are transformative practices that redefine the boundaries of rare diseases research. By building a foundation of coherent, accessible, and detailed data, the research community can unlock new horizons in understanding, diagnosing, and treating rare diseases. This concerted effort toward data harmonization empowers a collaborative, informed, and patient-centered approach to healthcare, marking a significant stride toward alleviating the burdens posed by rare diseases.
Data Visualization Techniques Unveil The Complexity Of Rare Diseases
The intricate mosaic of rare disease genetics and phenotypes necessitates sophisticated data visualization tools. Platforms such as RARe-SOURCE, with their comprehensive suite of resources including variant impact analysis and 3D protein structures, exemplify the integration of bioinformatics with clinical research. These visual analytics tools transcend traditional data interpretation methods, offering researchers and clinicians unparalleled insights into the genetic mechanisms driving rare diseases.
The evolution of data visualization, marked by the adoption of interactive dashboards and predictive modeling, leverages machine learning to dissect complex genomic data sets. This analytical prowess is crucial for anticipating disease trajectories and tailoring diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, marking a significant leap toward individualized patient care.
Adaptive Methods Of Content Validity Assessment
In recognizing the heterogeneity of rare diseases, adaptive methods for evaluating clinical outcome assessments (COAs) emerge as a vital component in capturing the multifaceted impact of these conditions on patients. Collaborative efforts with patient advocacy groups and disease registries enrich the research landscape with experiential data, guiding the development of interventions that resonate with the real-world challenges faced by patients.
This patient-centric research model not only elucidates the subjective dimensions of rare diseases but also aligns scientific inquiry with the priorities and needs of those it aims to serve. By grounding research in the lived experiences of patients, we forge a path toward therapeutic innovations that are both effective and empathetic, heralding a new era in the management of rare diseases.
The integration of innovative research methodologies, coupled with the standardization of data and utilization of advanced visualization techniques, represents a holistic strategy in addressing the complexities of rare diseases. This multifaceted approach, underscored by scientific rigor and a patient-centric ethos, holds the promise of transforming the landscape of rare disease research. Through meticulous adaptation to the unique intricacies of rare conditions, this strategy aims to expedite breakthroughs in diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. By aligning research endeavors with the distinctive requirements of rare diseases, we aspire to accelerate scientific advancements that translate into tangible benefits for patients, ultimately enriching their health outcomes and overall quality of life.
References:
- Mascalzoni, D., et al. (2021). "Rare diseases research: expanding collaborative translational research opportunities." Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 16, 1-10.
- Rodriguez-Monguio, R., et al. (2014). "Data standardization for clinical research: A model based on the experience with the rare disease registry for thalassemia." Journal of Registry Management 41(1), 14-18.
- Atalaia, A., et al. (2020). "A guide to approaching regulatory considerations for lentiviral-mediated gene therapies." Human Gene Therapy Methods 31(5), 209-222.
- Kodra, Y., et al. (2018). "Data quality in rare diseases registries." Public Health Genomics 21, 1-10.
- Ameratunga R, Woon ST, Gillis D, Koopmans W, Steele R. Global Distribution of Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) in the Context of Other Rare Diseases: An Observational Study. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020;15(1):202. doi:10.1186/s13023-020-01492-0.
About The Author:
 With over two decades of experience spanning clinical operations in the healthcare industry, Jeff Parke brings a wealth of expertise in strategic planning, operational efficiency, and cross-functional leadership. Throughout his career, Mr. Parke has been driven by a passion for driving positive change and innovation in clinical research. Mr. Parke has a proven track record of successfully managing large-scale projects and transformation programs, navigating complex regulatory landscapes, and fostering collaboration across diverse stakeholders. His commitment to excellence and dedication to advancing the field of clinical operations have been evident in his ability to drive impactful initiatives and deliver measurable results.
With over two decades of experience spanning clinical operations in the healthcare industry, Jeff Parke brings a wealth of expertise in strategic planning, operational efficiency, and cross-functional leadership. Throughout his career, Mr. Parke has been driven by a passion for driving positive change and innovation in clinical research. Mr. Parke has a proven track record of successfully managing large-scale projects and transformation programs, navigating complex regulatory landscapes, and fostering collaboration across diverse stakeholders. His commitment to excellence and dedication to advancing the field of clinical operations have been evident in his ability to drive impactful initiatives and deliver measurable results.
